Loading blog post...
Understanding Agent-Driven Workflows Across Smart Contracts and Onchain Systems
Web3 is moving beyond manual interactions toward a mature ecosystem of agent-driven workflows. Unlike traditional bots that follow rigid scripts, autonomous agents in Web3 are state-aware entities that coordinate complex logic across smart contracts, data feeds, and governance rules. By acting as a sophisticated control layer, these agents enable real-time protocol responsiveness and automated risk mitigation while remaining strictly bounded by onchain security constraints. This shift represents the evolution of decentralized operations, turning passive protocols into adaptive, continuous networks.
Web3 systems are now entering a new phase of maturity. Static smart contracts and manual interactions are giving way to dynamic, self-operating systems where software agents observe conditions, make decisions, and trigger execution autonomously. These systems are commonly described as agent-driven workflows, and they are becoming foundational to how modern onchain applications operate.
At the center of this shift are autonomous agents in Web3 - entities that coordinate logic across smart contracts, data feeds, governance rules, and external signals without relying on constant human input. When combined with smart contract orchestration and decentralized agent infrastructure, these workflows enable blockchain automation at a level that was impossible just a few years ago.
This blog explains how agent-driven workflows function across smart contracts and onchain systems, why they matter, and what differentiates experimental setups from production-grade onchain agent systems.

What Agent-Driven Workflows Actually Mean in Onchain Environments
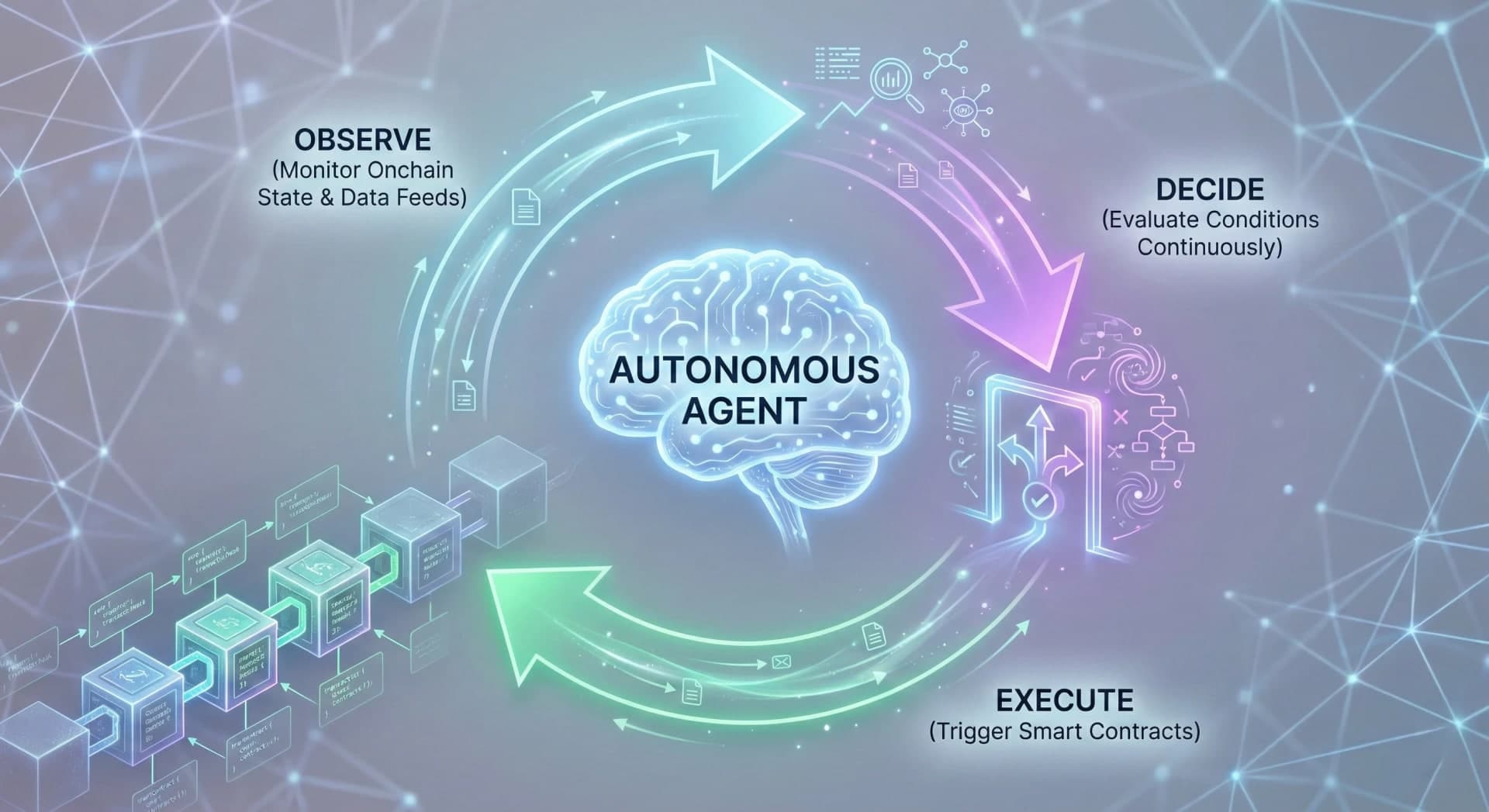
Agent driven workflows are basically setups where you hand off decisions and actions to software agents that follow certain rules. In the onchain world, like in Web3, they do not take over from smart contracts at all, they just kind of work together with them, coordinating things.
Rather than users manually triggering every action, agents can:
- monitor onchain and offchain state
- evaluate conditions continuously
- initiate transactions when criteria are met
- manage multi-step execution flows
This allows protocols to react in real time instead of waiting for human intervention. The result is a system that feels alive, constantly observing, deciding, and acting.
Our Web3 automation advisory focuses specifically on agent-based coordination models. Consult now.

Why Autonomous Agents in Web3 Are More Than Simple Bots
It’s pretty crucial to distinguish between autonomous agents and the usual bots you see around. Bots are basically just scripted things, they follow a set path without much variation.
With autonomous agents in Web3, it feels like they run inside these constraint systems and adjust their actions as the situation evolves. That adaptability sets them apart and makes them not so simple.
A Web3 agent typically:
- reads from multiple smart contracts
- interprets protocol rules
- reacts to state changes instead of schedules
- executes only when rules allow
Here, pointers help clarify the distinction:
Unlike bots, agents are:
- state-aware, not time-based
- rule-constrained, not hard-coded
- auditable through onchain execution
This is why agents are increasingly used in treasury management, liquidation systems, governance automation, and protocol risk mitigation.
Designing agents that behave predictably under adversarial conditions requires deep protocol and security expertise. That’s why teams work with EthElite’s smart contract development team to build agent systems they can rely on.
Onchain Agent Systems as the Control Layer for Smart Contract Orchestration
Smart contracts are deterministic and passive, they execute only when called. Onchain agent systems acts as the control layer, deciding when those contracts get invoked and how it happens.
In practice, smart contract orchestration means:
- sequencing multiple contract calls
- enforcing execution order
- handling conditional branching
- managing retries and failures
Agents do not go for monolithic contracts that try to handle every single thing at once. They coordinate smaller contracts instead, the kind that focus on just specific parts and that builds into a bigger workflow overall.
This orchestration model improves maintainability, security and upgrade flexibility across complex onchain systems.

Blockchain Automation Becomes Possible Only With Agent Coordination
Smart contracts logic is static in how they work. Blockchain automation though, requires something that can continuously observe the system and take action without manual triggers.
Agent-driven automation enables:
- automatic liquidity rebalancing
- governance execution after vote thresholds
- parameter adjustments based on market conditions
- risk responses during abnormal activity
These workflows significantly reduce operational overhead while increasing protocol responsiveness.
Well-designed agent-driven workflows do not act freely, they are bounded by smart contracts that define strict limits on what actions are allowed.
Decentralized Agent Infrastructure Prevents Hidden Control
One of the biggest risks with automation is centralization. If a single server controls agents, the system quietly reintroduces trust.
Decentralized agent infrastructure solves this by:
- distributing agent execution
- using multiple independent operators
- anchoring authority onchain
- enabling transparent validation of actions
Here, pointers highlight why decentralization matters:
Without decentralization:
- automation becomes opaque
- agents become privileged actors
- failure modes become catastrophic
With decentralized infrastructure, agents operate as part of the protocol and not above it.

Agent-Driven Workflows Improve Governance Without Removing Humans
People sometimes get the idea that agent-driven workflows just get rid of human involvement altogether. That is however not the reality. They actually build on what humans already do, making things better without taking over.
In governance systems, agents:
- monitor vote outcomes
- execute proposals automatically
- enforce timelocks and safety checks
- prevent partial or inconsistent execution
So, AI agents make sure governance decisions happen exactly as approved. No manual is execution needed.
This reduces friction in governance. If designed right, they keep community control intact, which is important.
Security Boundaries Are Central to Onchain Agent Systems
AI Agents can be really powerful, which makes security boundaries non-negotiable. A well-designed agent-driven workflow clearly defines what an agent can never do, regardless of conditions.
These boundaries usually include:
- spending caps
- action whitelists
- rate limits
- emergency stop mechanisms
Agents do not replace security, they operate within it.
Why Agent-Driven Workflows Signal the Next Phase of Web3 Maturity
Early Web3 focused on decentralizing ownership and execution. The current phase focuses on decentralizing operations. Agent-driven workflows represent that evolution.
When autonomous agents in Web3 are properly constrained, orchestrated, and decentralized, they transform protocols from static systems into adaptive networks that can operate continuously without sacrificing trust.
Autonomous agents in Web3 can shift protocols in a big way if handled right. When they are properly constrained, orchestrated, decentralized, it turns old static systems into more adaptive systems. Networks that just keep going without stopping, and trust stays intact.
This shift is less about novelty and more about sustainability at scale.
FAQ: Agent-Driven Workflows and Onchain Systems
Q: Are agent-driven workflows the same as smart contracts?
A: No. Agents coordinate and trigger contracts; contracts enforce rules.
Q: Do autonomous agents in Web3 require AI?
A: Not necessarily. Most agents are rule-based rather than model-driven.
Q: Is blockchain automation safe?
A: Yes, when agents operate within strict onchain constraints.
Q: Can onchain agent systems be decentralized?
A: Yes. Execution can be distributed without central control.
Q: Where are agent-driven workflows used today?
A: Treasuries, DeFi risk systems, governance execution, and protocol operations.
Conclusion
Share with your community!